IIFT
- Home
- IIFT
Indirect immunofluorescence used at Rayan Specialised Laboratory tests (IIFT) from EUROIMMUN
Unrivalled quality and variety.
Advantages of EUROIMMUN IIFT:
- Unrivalled standardisation of IIFT due to BIOCHIP technology with highest quality on millimetre-sized fragments.
- Combination of BIOCHIPs in Mosaics on one reaction field for multiplex testing.
- Comprehensive product range for autoimmune and infection diagnostics based on BIOCHIPs with cultured cells, antigen dots (EUROPLUS), antigen-expressing cells and tissue sections.
- Test kits containing ready-for-use reagents that are exchangeable between products with bar and colour codes for secure manual and automated processing.
- Various test kit formats for different sample throughputs: slides with 5, 10 and 50 reaction fields.
- Universal incubation schemes for uncomplicated combined processing of different parameters.
- DataMatrix codes on all slides for complete traceability.
- Brilliant fluorescence images due to incubation using TITERPLANE technology.
Test Principle
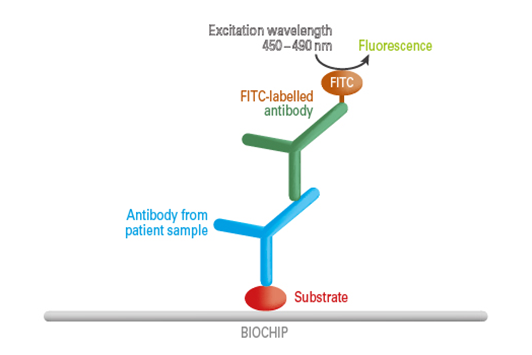
In the first incubation step, specific antibodies from the diluted patient sample bind to the solid-phase bound antigens. In the next step, a fluorescein (FITC)-labelled antibody (conjugate) binds to the specific antibodies from the patient sample. By excitation with the respective wavelength, the complex can be made visible at the fluorescence microscope. The test processing is manual, semi- or completely automated.
ANA Global (IIF):
The gold standard for the determination of ANA is the indirect immunofluorescence test (IIFT) with human epithelial cells (HEp-2), which is known for its high sensitivity and specificity. Positive and negative samples produce a large signal difference. In the microscopic evaluation it is possible to establish precisely how an indicator dye (generally fluorescein) is distributed in the tissue or the cells. A typical fluorescence pattern is produced for every bound autoantibody, depending on the location of the individual autoantigens.
The first international consensus on standardised nomenclature of HEp-2 cell patterns in indirect immunofluorescence (ICAP, www.anapatterns.org) defined fifteen nuclear patterns and nine cytoplasmic patterns which are relevant for the diagnosis of various autoimmune diseases.
Furthermore, the consensus recommends that autoantibodies detected in indirect immunofluorescence be confirmed by additional specific tests (e.g. ELISA, line blot). The exclusive use of these monospecific test methods is inadequate for the determination of autoantibodies against cell nuclei, as not all relevant antigens are available in a purified form as yet. Thus, the corresponding ANA can only be detected by IIFT.
ANA Indirect Immunofluorscence patterns & clinical association:
| Pattern | Clinical Significance |
| Homogenous | SLE, Drug induced Lupus, Rheumatoid arthritis, Systemic Sclerosis. |
| Homogenous with nuclear ring | SLE, particularly when the disease active. |
| Coarse Speckled | SLE, Mixed connective tissue disease, Sharp syndrome. |
| Fine speckled | SLE, Sjogren’s Syndrome, Sub acute cutaneous Lupus, Scleroderma. |
| Nucleolar | Polymyositis, scleroderma overlap Syndrome |
| Cytoplasm Filamentous | CAH : Chronic active auto immune hepatitis and other un known clinical association. |
| Centromere | Progressive systemic Sclerosis, limited form. |
| Cytoplasmic granular | PBC: Primary Liver cirrhosis, PM : Polymyositis and other unknown clinical association. |
| Centerioles | Progressive systemic Sclerosis |
| Golgi apparatus | SLE, Sjogren’s Syndrome,Rheumatoid arthritis. |
| Nucleoplasm dots | PBC: Primary Liver cirrhosis, Rheumatic disease |
| Nuclear dots | PBC: Primary Liver cirrhosis, Rheumatic disease, SLE, Sjogren’s Syndrome |
| Several nuclear dots | PBC: Primary Liver cirrhosis, Rheumatic disease |
| Spindle fibers | Rheumatic disease |
| Midbody | Un known clinical association |
| Anti nuclear membrane | CFS: Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, CAH: Chronic active auto immune hepatitis, colegenoses. |
