ELISA
- Home
- ELISA
ELISA used at Rayan Specialised Laboratory EUROIMMUN ELISAs
Precise quantitative and semiquantitative determination.
- Comprehensive product rangefor autoimmune and infection diagnostics, antigen detection and therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM).
- Highest test qualitydue to in-house antigen design and production.
- No additional reagents required, all necessary reagents included in the test kits.
- Ready for use reagents, exchangeable between products with bar and colour codes for secure manual and automated processing.
- Universal instead of individual incubation schemes enable uncomplicated combined processing of different parameters.
- Optimised for fully automated processing using EUROLabWorkstation ELISA, EUROIMMUN Analyzer I or EUROIMMUN Analyzer I-2P.
Test principle
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) from EUROIMMUN use antigens or antibodies coated on a polystyrene plates with 96 wells as a solid phase to bind specific antibodies or antigens in patient samples through an enzymatic colour reaction. The processing can be manual, semi-automated or fully automated. Monospecific ELISAs are used for semi-quantitative or quantitative determination of antibodies or antigens. Semi-quantitative detection of various antibodies on a single microplate strip is achieved using profile ELISAs. Here, the solid phase is coated with an antigen mixture. The antibodies can be detected semi-quantitatively. Afterwards, a differentiated detection must be performed with the respective monospecific assay.
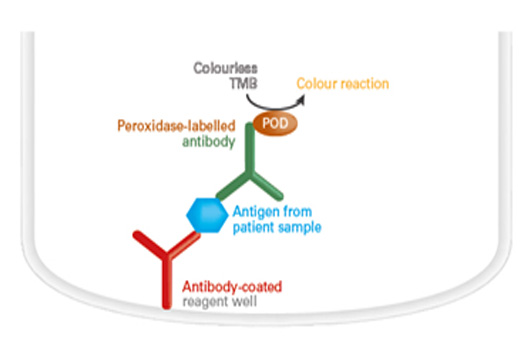
Antibody detection by ELISA (competitive ELISA)
The antigen-coated reagent wells of the microplate are incubated with diluted patient samples. If a sample contains specific antibodies directed against the antigen, these bind to the antigen-coated reagent wells and inhibit the binding of a biotin-labelled artificial molecular which is added to the reagent well in a subsequent step. Afterwards, peroxidase-labelled avidin is added which binds to the biotin-labelled molecules. In the third incubation step, the peroxidase and the peroxidase substrate tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) catalyse a colour reaction. The intensity of the resulting colour solution is inversely proportional to the antibody concentration in the patient sample within the measurement range and can be converted into a concentration by means of a calibration curve in the quantitative tests.
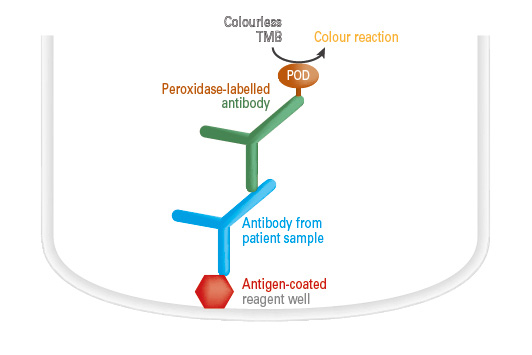
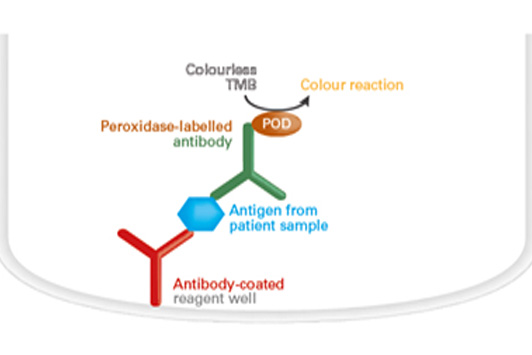
Antigen detection by ELISAs (sandwich ELISA)
The reagent wells of the microplate coated with monospecific antibodies are incubated with diluted patient samples. If the sample contains the respective antigens, these bind to the antibody-coated reagent well. In a further step, a peroxidase-labelled antibody (conjugate) is added, which binds to another epitope of the antigen. When the peroxidase substrate tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) has been added, the peroxidase catalyses a colour reaction. The intensity of the results colour solution is proportional to the antigen concentration in the patient sample within the measurement range and can be converted into a concentration by means of a calibration curve in the quantitative tests.
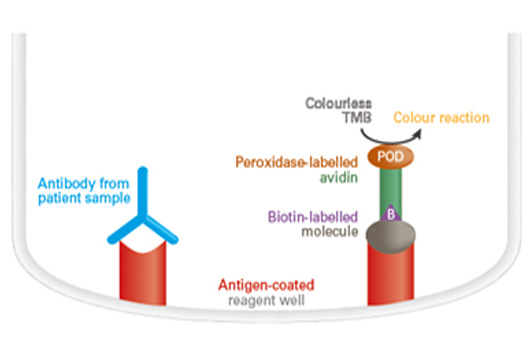
Antigen detection by ELISA (competitive ELISA)
The reagent wells of the microplate coated with monospecific antibodies are incubated with diluted patient samples and a defined amount of biotin-labelled antigen. If the sample contains the corresponding antigens, these compete with the biotin-labelled antigen for the binding sites in the antibody-coated reagent well. Afterwards, peroxidase-labelled streptavidin is added (conjugate) which binds to the biotin-labelled antigens. When the peroxidase substrate tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) has been added, the peroxidase catalyses a colour reaction. The intensity of the results colour solution is inversely proportional to the antigen concentration in the patient sample within the measurement range and can be converted into a concentration by means of a calibration curve in quantitative tests.